Data types specify how we enter data into our programs and what type of data we enter. C language has some predefined set of data types to handle various kinds of data that we use in our program. These datatypes have different storage capacities.
C language supports 2 different type of data types Primary data types and Derived data types.
These are fundamental data types in C namely integer(int), floating(float), charater(char) and void.
Derived data types are like arrays, functions, structures and pointers. These are discussed in detail later.
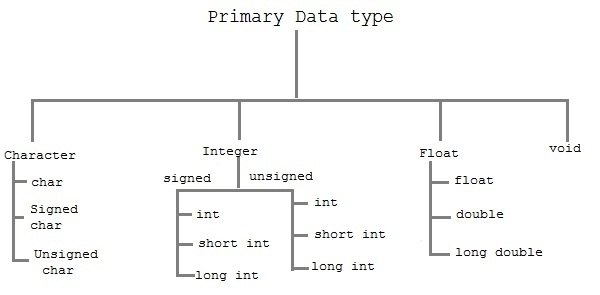
Character types are used to store characters value.
Size and range of Integer type on 16-bit machine
| Type | Size(bytes) | Range |
|---|---|---|
| char or signed char | 1 | -128 to 127 |
| unsigned char | 1 | 0 to 255 |
Integers are used to store whole numbers.
Size and range of Integer type on 16-bit machine
| Type | Size(bytes) | Range |
|---|---|---|
| int or signed int | 2 | -32,768 to 32767 |
| unsigned int | 2 | 0 to 65535 |
| short int or signed short int | 1 | -128 to 127 |
| long int or signed long int | 4 | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| unsigned long int | 4 | 0 to 4,294,967,295 |
Floating types are used to store real numbers.
Size and range of Integer type on 16-bit machine
| Type | Size(bytes) | Range |
|---|---|---|
| float | 4 | 3.4E-38 to 3.4E+38 |
| double | 8 | 1.7E-308 to 1.7E+308 |
| long double | 10 | 3.4E-4932 to 1.1E+4932 |
void type means no value. This is usually used to specify the type of functions. For Example void main()
Ask Question